Control Panel User's Guide
Main Window Layout
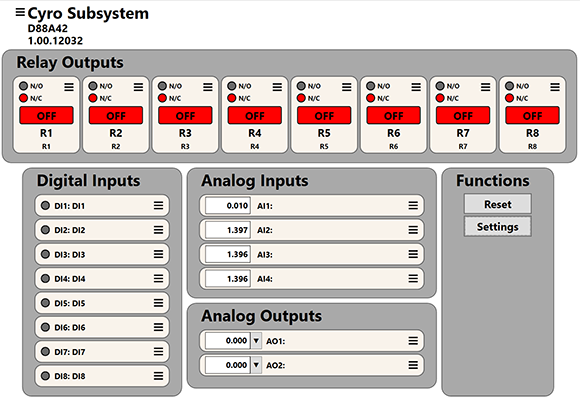
The Main Window provides a comprehensive view of the current system status and control interface. It is divided into clearly labeled sections for interacting with hardware components and managing system functions.
The layout includes:
- Relay Outputs (Top row, center)
- Digital Inputs (Lower left)
- Analog Inputs (Lower center)
- Analog Outputs (Lower right center)
- Functions (Lower right)
Each I/O element includes status indicators and allows user interaction such as toggling, renaming, or configuration.
Relay Outputs
Eight relay output channels (R1-R8) are displayed in individual blocks. Each block shows:
-
Current State:
- Red = OFF
- Green = ON
- Contact Type: Radio buttons indicate Normally Open (N/O) or Normally Closed (N/C)
- Label: Each relay includes a user-defined name (e.g., Power, Valve, Motor, Pump)
Click the menu button next to any relay to open the properties panel. This panel allows you to customize the name of the input (e.g., vent valve, scroll pump, power enable).
Relay Properties
Each relay can be individually configured using the Relay Properties Window. Options include:
- Name: Assign a descriptive label for easy identification

Digital Inputs
This section shows eight digital input channels (DI1-DI8). Each displays:
- A green circle if the input is active (logical HIGH)
- A gray circle if inactive (logical LOW)
- A user-defined label (e.g., Power ON, Valve OPEN)
Right-clicking a digital input opens the Digital Input Properties Window, where the label can be edited.
Digital Input Properties
Click the menu button next to any digital input to open the properties panel. This panel allows you to customize the name of the input (e.g., door status, valve open, motor running).
- Name: Enter a user-defined label for the input (e.g., "TEST R1 - NO")
- Auto Save: The name is preserved across sessions if autosave is enabled

Analog Inputs
Up to four analog input channels (AI1-AI4) are shown, each with:
- A numeric display of the current input value
- A user-defined label and unit (e.g., Motor Temperature (ºC), Pump Speed (RPM))
- A context menu button to access the Analog Input Properties
Analog inputs can be configured for calibration, filtering, and custom units.
Analog Input Properties
Clicking the menu button on the right side of any analog input opens the properties panel. This panel allows you to customize the behavior and display of the selected channel.
- Name: Set a user-defined label (e.g., "Pump Speed" or "Temp Sensor")
- Units: Define engineering units like ºC, PSI, RPM
- Filter: Enable signal smoothing using a low-pass filter
- Enable Calibration: Apply a two-point linear calibration
Calibration Fields:
- Input 1 / Corrected 1: First calibration point (raw input vs desired output)
- Input 2 / Corrected 2: Second calibration point

Analog Outputs
Two analog output channels (AO1 and AO2) appear at the bottom right of the analog I/O area. Each includes:
- A numeric field showing the current output value
- A drop-down or slider for adjusting the value
- A user-defined label and unit (e.g., Motor Speed (RPM))
- A context menu button for the Analog Output Properties
Analog outputs can be calibrated to convert display values into actual voltage output.
Analog Output Properties
Click the menu button next to any analog output channel to open the properties panel. This dialog lets you define how the channel is labeled and scaled.
- Name: Set a descriptive label for the output (e.g., "Pump Setpoint")
- Units: Specify the units for user-facing display (e.g., V, PSI, RPM)
- Enable Calibration: Apply a linear mapping between voltage and display value
Calibration Fields:
- Voltage Out 1 / Display Value 1: Defines the first point on the calibration curve
- Voltage Out 2 / Display Value 2: Defines the second point

Functions: Reset and Settings
This section includes two system-level functions:
-
Reset:
- Immediately sets all outputs to their configured default state
-
Settings:
- Opens the Settings Window to adjust system-wide parameters, such as:
- Sampling interval
- Default relay states
- Startup behavior
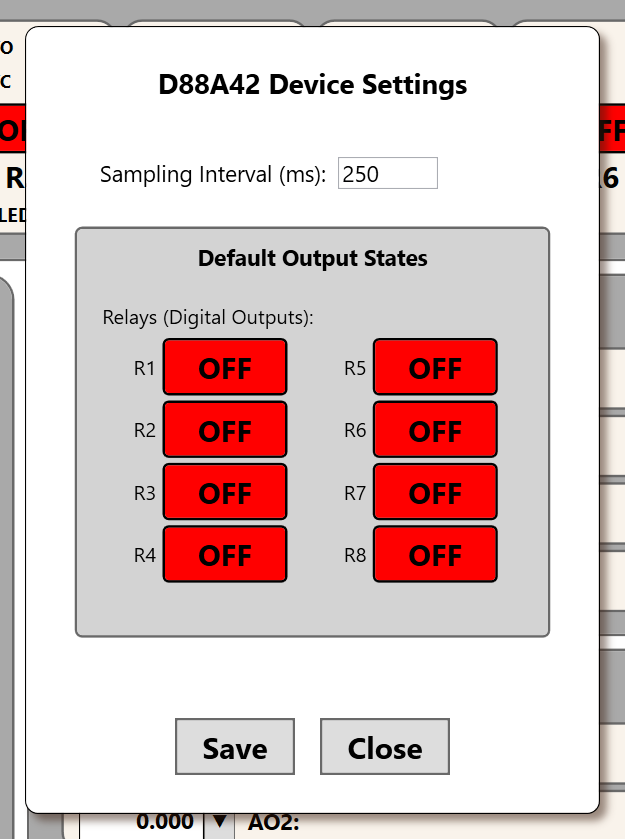
Settings Window
Clicking the Settings button opens the Device Settings window, where you can control timing and default startup behavior.
- Sampling Interval: Sets the rate (in ms) at which the system polls all inputs and updates outputs.
- Default Output States: Sets the initial state of all relays (R1-R8) on startup or reset.
- Save: Saves the selected sampling interval and relay defaults to persistent storage.
- Close: Exits the window without saving changes.
Troubleshooting
Relays are unresponsive
Check if 120VAC power is connected. This is required for the relays to function correctly.
The window is blank when the Control Panel is launched
- This usually means the USB cable is not properly connected. Ensure it is securely attached at both ends and relaunch the application.
- The D88A42 might be open in another software instance.
Digital inputs are not responding
- The input voltage may not be high enough to register as "on"
- The external input circuit may not share a common ground with the Control Panel
Analog inputs show unexpected values
- The sensor may not be connected properly.
- The input may not be calibrated, or the wrong calibration values were entered.
- Noise in the wiring could be affecting readings - try enabling the filter.
- The external device might need a common ground with the control panel.
Analog outputs don't control the external device
- Check the calibration mapping - a bad scale could send unexpected voltages.
- The device might need a common ground with the control panel.
The app is slow or unresponsive
- The sampling interval might be set too low. 250ms is a good sampling rate. Set this value in the settings window on the main window
PID Control
Purpose
The PID Control system provides automated regulation of analog output channels using real-time feedback from analog inputs. Each loop applies Proportional–Integral–Derivative (PID) logic to minimize the difference between a desired setpoint and the actual process value. This enables precise closed-loop control of temperature, pressure, flow, or other analog processes.
Accessing and Managing PID Loops
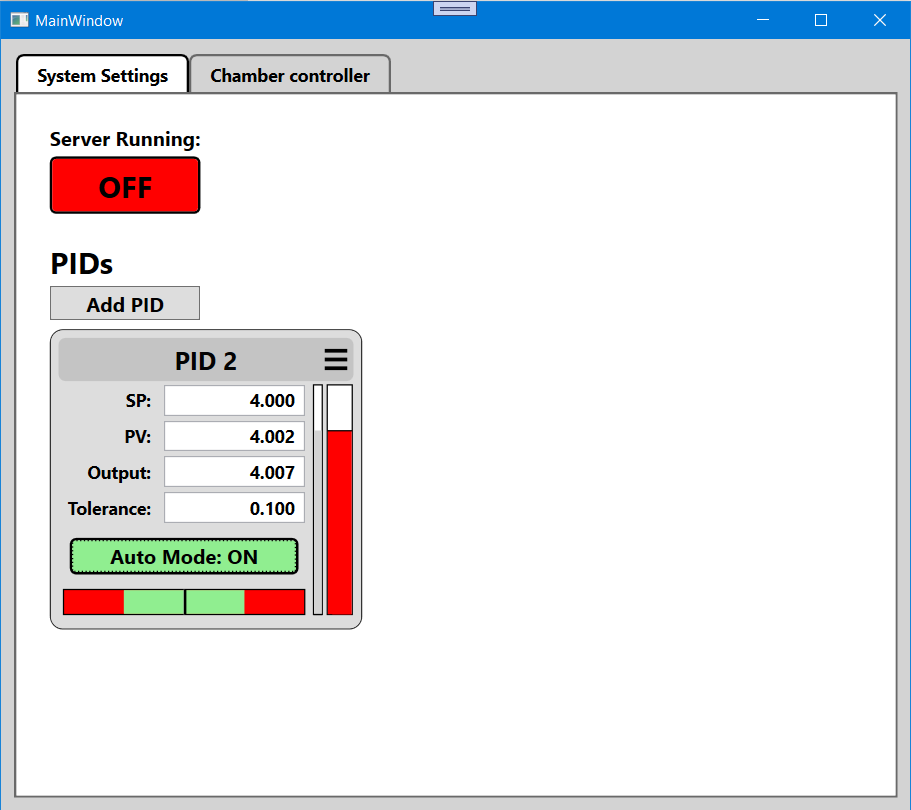
Go to the System Settings tab. Scroll to the PIDs section. Click Add PID to create a new loop. Each loop appears as a control panel with real-time data and a menu button (≡) for configuration.
PID Panel Overview
SP (Setpoint) – Desired target value.
PV (Process Value) – Current input value from the assigned analog input.
Output – Control signal applied to the output channel.
Tolerance – Defines acceptable PV deviation from the SP.
Auto Mode – Enables or disables automatic control.
Menu Button (≡) – Opens the configuration interface.
Visual Indicators
PV Bar (Red, Vertical – Far Right)
Displays the current Process Value on a vertical scale from PV Min (bottom) to PV Max (top). A taller red bar indicates a higher PV.
Output Bar (Gray, Vertical – Right of Center)
Shows the current Output level. The gray bar fills proportionally between Output Min and Output Max, indicating the strength of the control signal.
Tolerance Bar (Horizontal – Bottom)
Visualizes how close the PV is to the Setpoint. The black vertical line represents the setpoint. The green band shows when PV is within ±1× tolerance (on target). The red band shows when PV is within ±2× tolerance (approaching limits). If the PV moves outside the red, it is out of the tolerance range.
Configuration Panel
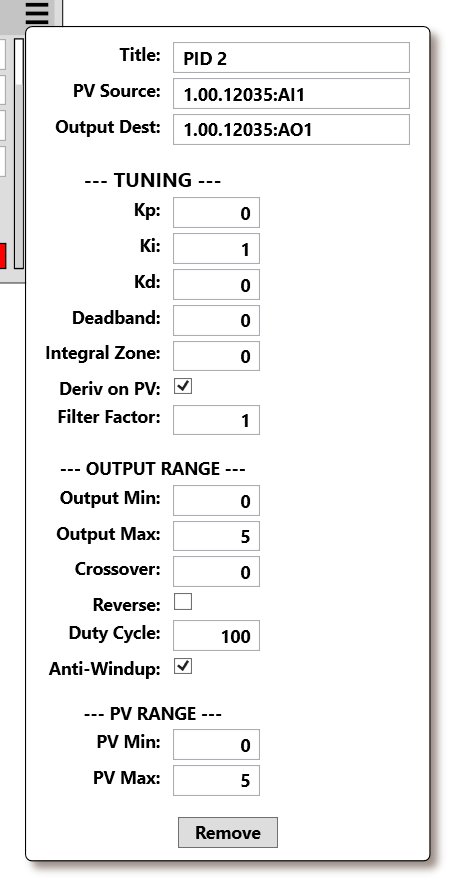
Title – Display name for the PID loop.
PV Source – Analog input address providing the process value.
Output Dest – Output address controlled by the PID loop.
Tuning Parameters
Kp – Proportional gain (current error).
Ki – Integral gain (accumulated error).
Kd – Derivative gain (rate of change).
Deadband – Suppresses output changes near SP.
Integral Zone – Restricts integral effect to small errors.
Deriv on PV – Applies derivative to PV instead of error.
Filter Factor – Smooths derivative response.
Output Range
Output Min / Max – Limits output voltage range.
Crossover – Determines direction of control action.
Reverse – Reverses the output logic (useful for cooling loops).
Duty Cycle – Scales output for pulsed control.
Anti-Windup – Prevents integrator from oversaturating the output.
PV Range
PV Min / Max – Defines scaling bounds for the Process Value input.
Runtime Behavior
PID loops run continuously at the configured sampling interval. In Auto Mode, the loop automatically calculates output. In Manual Mode, the output can be set directly by the user. Click Remove to delete a PID loop from the system.